Over the past 2 years, the adoption of generative AI applications like ChatGPT, Google’s Gemini, has accelerated at an extraordinary pace. Apart from enhancing productivity and streamlining content development, these technologies are redefining the very manner in which users seek and engage with information.
The conventional pattern of search, formerly characterized by the entry of keyword strings followed by a curated drill through ranked hyperlinks, is now giving way to AI-centric information exploration. Contemporary users now require, and increasingly assume, that even nuanced inquiries will yield immediate, coherent, and semantically organized responses. For marketers and content strategists, this paradigm evolution imposes an immediate and thorough reckoning with how generative AI reconfigures search engine optimization, failure to do so risks outdatedness in digital visibility and market relevance.
Rise of AI in Search and Content Discovery
Search has transitioned from rigid keyword phrases to fluid, conversational queries. The typical user no longer types “best laptops 2025” but reformulates the question to, “What are the best laptops under 80,000 rupees that excel in video editing and portability?”
Innovative AI search platforms like Google’s Search Generative Experience, Bing AI, and ChatGPT Browse now parse these intricate requests, delivering structured, citation-rich, and context-aware responses that span multiple dimensions of information.
Stats: 62% of users favor AI-generated summaries to classic search results, according to the 2024 Google Trends Report.
How ChatGPT and Gemini Are Changing User Behavior
ChatGPT and Gemini are reshaping the landscape of search and content engagement by moving beyond the limitations of keyword-driven queries. Both platforms are aligned to excel under the following circumstances:
- Natural conversation: Queries framed in everyday language that mirror dialogue
- Layered inquiries: Sequences of questions that build upon earlier responses
- Interdisciplinary linkage: Drawing parallels between disparate topics to surface relevant insights
Users now expect these engines to understand their underlying motives rather than match distinct terms. Consequently, information is presented in reformatted, scannable units like in bullet lists, comparative tables, concise summaries.
Key statistic: 81% of Gen Z report using AI chatbots for routine information-seeking, according to Think with Google, 2024.
This data signals a growing confidence in AI-generated replies, diminishing the need to peruse numerous search results. Marketers are therefore urged to reorient their strategies toward the mechanics of content delivery rather than the mechanics of discovery.
Impact of AI Tools on SEO Strategy
Traditional SEO vs AI-Optimized SEO
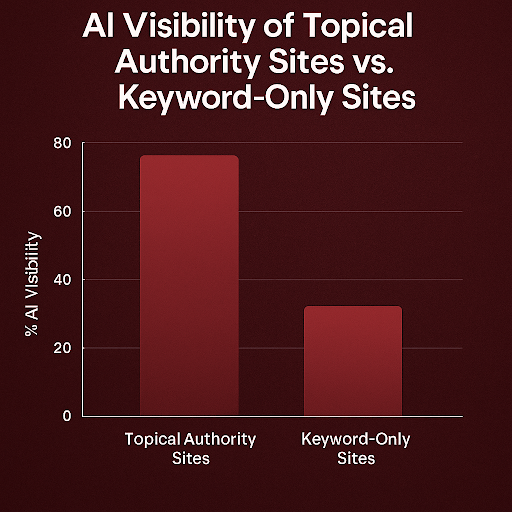
Where traditional SEO prized keyword density, backlinks, and on-page tags, the latest search-ranking strategies shaped by AI demand a new mindset. Advanced tools such as ChatGPT and Gemini now empower algorithms to favour contextual depth, semantic coherence, and recognised topical authority, rendering old tactics such as keyword density and sheer link volume obsolete. AI now seeks to grasp the underlying intent behind queries and to surface the most comprehensive, logically organised, and credible material possible. As a consequence, brands should now emphasise the construction of interlinked content clusters, the application of schema markup, the rigorous application of the EEAT framework—Expertise, Experience, Authoritativeness and Trustworthiness—and the design of clearly structured, answer-focused sections that AI can readily extract, attribute and feature within search results.
- Topical Authority > Keyword Repetition
- Semantic Relevance > Exact Matches
- Structured Answers > Long Paragraphs
Contemporary generative AI models, exemplified by ChatGPT and Gemini, preferentially extract information from repositories characterized by the following structural and semantic features:
- Thematic content is segmented into coherent, interlinked clusters, facilitating the model’s rapid identification of relevant subtopics.
- Information is presented in predefined, semantically tagged blocks—such as FAQs, stepwise instructions, and tabulated data—enabling rapid, granular parsing.
- Application of schema vocabulary (e.g., Schema.org) endows content with machine-readable metadata that contextualizes entities and relationships.
- The content is demonstrably underpinned by expertise, experiential knowledge, authoritativeness, and trustworthiness (EEAT), as increasingly scrutinized by qualitative and quantitative heuristics.
Empirical data from Ahrefs (2024) indicate that pages engineered around cohesive topical clusters exhibit a 45% heightened probability of being surfaced in AI-generated knowledge panels and direct-answer outputs.
Opportunities & Challenges for Marketers
Opportunities:
- Increased Citation Potential: Research demonstrating coherent structure and clear argumentation tends to be preferentially leveraged by advanced generative AI systems, exemplifying citation behavior characteristic of models such as ChatGPT and Perplexity.
- Accelerated Brand Recognition: The Gemini model incorporates proprietary brand references within relevant completions, enhancing the discoverability of client brands in conversational interfaces.
- Rising Standard for Source Material: The AI ecosystem continues to scale, creating an expanding appetite for authoritative, syntactically precise, and conceptually rich documents—thus inviting marketers to create content configured for immediate integration into generative output.
Challenges:
- Attribution Loss: Some AI tools can create summaries that pop up in search results or social feeds, letting readers get the gist without ever hitting your site.
- Originality Conflicts: When lots of businesses use the same language models, chances of multiple pieces sounding alike keep climbing.
- Content Freshness: Many models aren’t dialed into the web in real time, so info can lag behind. Marketers then need to keep revising important pages to avoid stale content.
How to Optimize for AI-First Content Discovery
To thrive within the rapidly evolving ecosystem shaped by generative AI, marketers and SEO specialists must overhaul their content-blueprint philosophies so that they resonate with the retrieval and presentation mechanics employed by generative agents such as ChatGPT, Gemini, Bing AI, and Google SGE. The prior paradigm—grounded in isolated keyword prominence and backlink acquisition—has yielded to an AI-aided discovery plane that gauges the corpus as a multidimensional lattice, assessing topical coherence, internal architecture, and authoritative provenance in concert.
Optimization must therefore pivot from a narrow emphasis on discrete keywords or featured snippets to an expansive treatment of subject matter that foregrounds topical breadth, semantic depth, and machine-parseability. Generative intelligences demonstrate a marked preference for hierarchically structured information that anticipates, and sequentially fulfills, multifaceted user intents, decomposes intricate queries into interlinked, granular subsections, and can be distilled into confident, retrieval-ready summaries or attributions within conversational exchanges.
Here’s how:
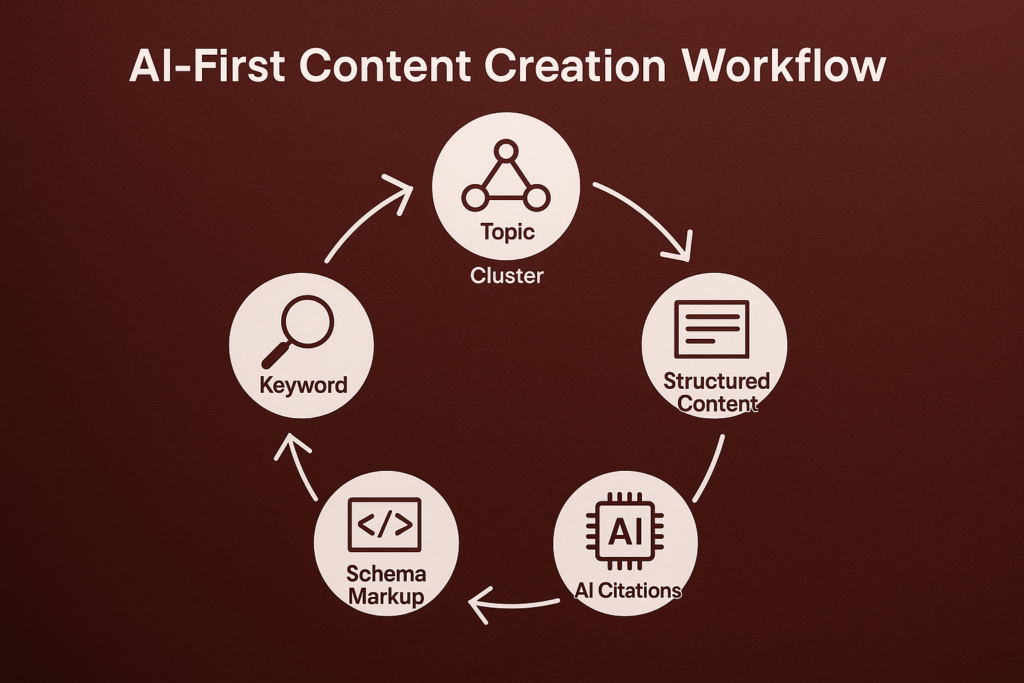
1. Build Topic Clusters
Establish content hubs centered on principal domains. A data science portal might feature:
- Introductory overviews on foundational concepts
- In-depth explorations of advanced algorithms and methodologies
- Applied case studies documenting real-world implementations
- Curated FAQs and actionable checklists for practitioners
Such organization enables algorithms to favor material that is cohesive, interrelated, and comprehensive.
2. Use Schema Markup and Structured Blocks
- Implement Structured Data
- Apply [`FAQ`](https://schema.org/FAQPage), [`HowTo`](https://schema.org/HowTo), [`Article`](https://schema.org/Article), and [`Product`](https://schema.org/Product) schemas to relevant pages
- Ensure JSON-LD scripts are placed within `<head>` or immediately after the opening `<body>`
- Organize Content Visually
- Use `<h1>` for main titles, `<h2>` for section titles, and `<h3>` for subsections
- Present lists with `<ul>` or `<ol>` and use `<table>` for tabular data
- Avoid excessive indentation or blank lines to retain clean rendering
- Populate Metadata and Alt-Texts
- Fill `<meta name=”description”>` with a concise summary relevant to each page
- Assign `alt` attributes to all `<img>` tags, describing the content or function of the images
- Use `schema:image` within structured data to link to the corresponding images
3. Focus on EEAT
- Incorporate biographies that contextualize each author’s academic and professional qualifications, specifying terminal degrees, institutional affiliations, and relevant research or practice experience.
- Adopt a uniform citation style throughout the manuscript, and list all consulted sources at the end, including books, journal articles, and other materials, thus ensuring traceability and academic rigor.
- Commit to the ongoing circulation of literature that has undergone structured evaluation by scholars in the respective fields, thereby fostering an environment of reliable and cumulative knowledge production.
4. Optimize for SERP Features
- Get Featured Snippets, PAA, and Knowledge Panels
To earn a Featured Snippet, a PAA box, or a Knowledge Panel, you need to give clear, short answers to questions people ask. Use bullet points for quick facts and put important phrases in bold so they stand out.
- Use Definitions and Stats
- Definition: A Featured Snippet is a boxed answer that shows above the search results.
- Stat: Featured Snippets drive 10-15% of extra clicks to websites.
- Stat: Google shows PAA questions for 60% of searches.
Keep your answers to 40 words or fewer and start with the keyword people search for.
- Highlight Key Statements
Make your main points pop by bolding them. For instance:
- Videos in Featured Snippets can boost your visibility.
- Clear lists or tables tend to get selected.
Clear language and bold keywords increase your chance of being pulled into rich answer boxes, helping your content stand out.
5. Use AI for Gap Analysis
Tools such as ChatGPT, Clearscope, and Frase can be useful:
- Analyzing the competition
- Identify missing semantically-related phrases
- Make suggestions for improved content organization
Conclusion
ChatGPT, Gemini, Claude, and other AI tools are now content gatekeepers rather than merely writing assistants. They decide how information is presented and what information reaches users.
It is no longer optional to comprehend the impact of AI technologies on SEO; doing so makes the difference between being visible and invisible in search results.
Content producers need to include trust, relevance, and structure into everything they post as SEO shifts from keyword density to contextual depth and topical authority.
It’s time to change your approach if you work as a digital marketer. Don’t limit your optimization to Google. Make AI your priority.