Microsoft has launched the AI Performance dashboard inside Bing Webmaster Tools as a public preview. It shows publishers how often their content is cited in AI-generated answers across Microsoft Copilot, Bing AI summaries and select partner integrations.
This is the first time a major search platform has offered dedicated, first-party reporting on generative AI citation activity. Microsoft describes it as an early step toward Generative Engine Optimization (GEO) tooling, marking the formal separation of AI visibility from traditional search metrics.
What the AI Dashboard Data: How It Track & Compares to Google
The dashboard introduces five metrics focused entirely on how AI systems cite your content. These do not indicate ranking, prominence, or how a citation appeared within an answer, only that your content was used as a source.
- Total Citations: Counts how often your site appeared as a source in AI-generated answers during the selected time period. This is a frequency metric, not a quality or prominence indicator.
- Average Cited Pages: Shows the daily average of unique URLs from your site referenced across AI experiences. Higher numbers suggest broader topical coverage being recognized by AI retrieval systems.
- Grounding Queries: This is the most significant feature. Grounding queries are not the exact phrases users typed, they are the internal retrieval phrases Bing’s AI system generated to find candidate content before building an answer. This provides a direct window into how AI systems interpret and search for your content. Microsoft notes this is a sample, not a complete dataset.
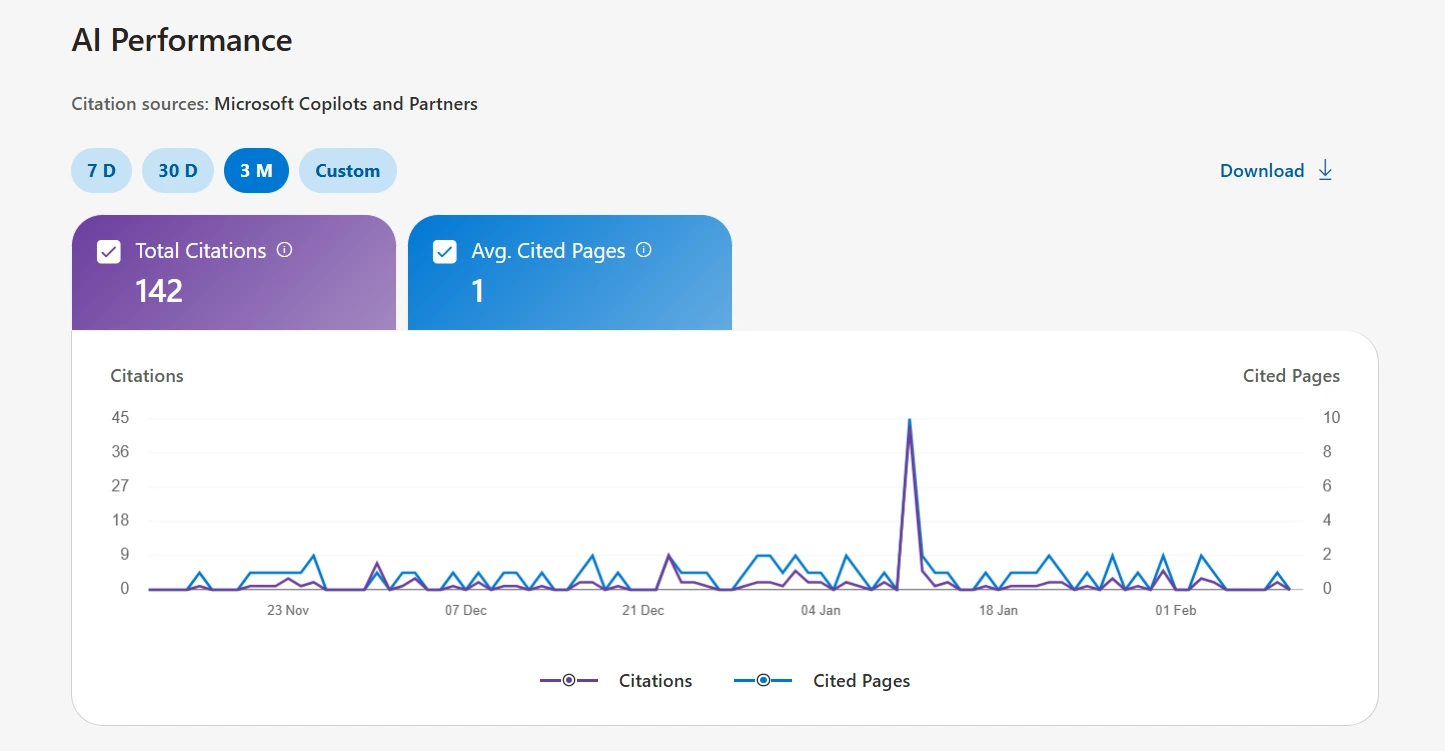
- Page-Level Citation Activity: Breaks down citation counts by individual URL, revealing which pages AI systems reference most and least often.
Visibility Trends Over Time: A timeline charting citation fluctuations across AI surfaces, enabling publishers to spot growth patterns, seasonal effects, and the impact of content updates.
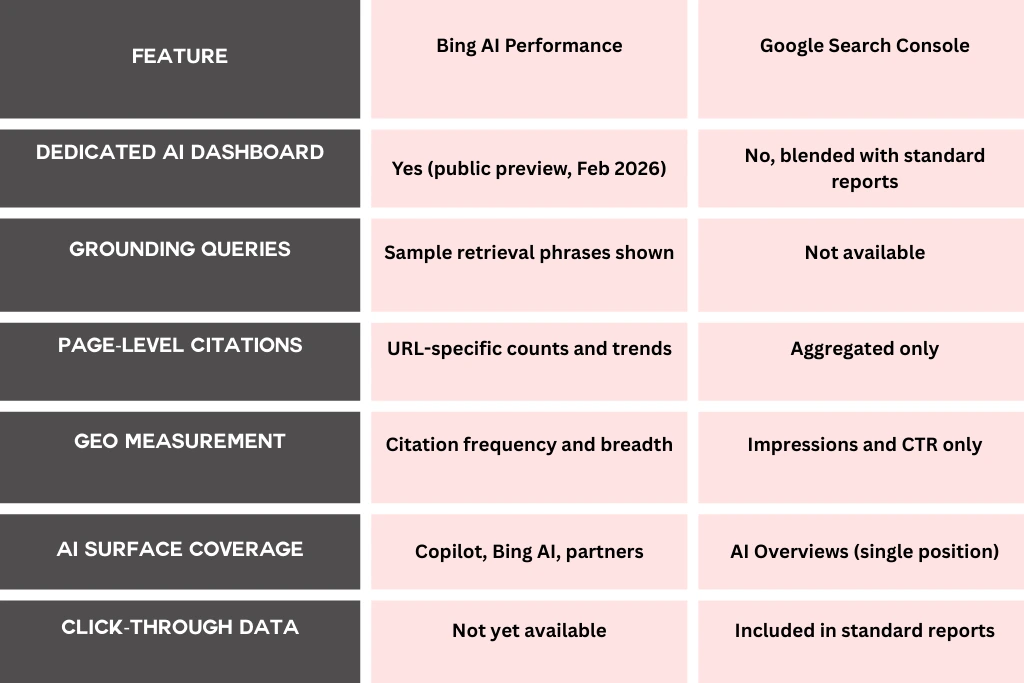
Bing AI Performance vs. Google Search Console
Google includes AI Overviews and AI Mode data within Search Console’s standard Performance report. However, it does not offer a dedicated AI citation dashboard, URL-level citation counts, or grounding query visibility. All links within a single AI Overview share one ranking position.
Bing isolates AI performance as a separate measurement layer, treating generative answers as a distinct ecosystem rather than another search feature.
Feature Comparison: Bing AI Performance vs. Google Search Console
What Publishers Should Do Now
The dashboard does not yet show clicks, traffic, or conversion data. However, it provides actionable signals for content optimization.
- Audit Your Cited Pages: Identify which URLs are cited most frequently. Expand topical depth around those pages by building supporting content within the same entity cluster.
Use Grounding Queries as a Retrieval Keyword Tool: Grounding queries reveal how Bing’s AI interprets your content. If a phrase appears repeatedly, ensure it is reflected in your headings, opening paragraphs, and structured data. These are direct retrieval signals.
- Improve Content Structure for AI Retrievability: Clear headings, concise definitions, FAQ sections, comparison tables, and evidence-backed claims improve how AI systems extract and reference your content.
- Maintain Entity Consistency: Align text, images, metadata, and structured data (Organization, Article, FAQ schema) so AI systems can confidently associate your pages with specific entities and topics.
- Implement IndexNow for AI Freshness: Microsoft explicitly links IndexNow to AI citation freshness. The protocol notifies participating search engines when content is updated, enabling faster ingestion into AI retrieval systems. This is particularly important because Bing’s index also powers ChatGPT’s web browsing and Microsoft Copilot.
- Register with Bing Places: For location-based AI queries, accurate business information in Bing Places for Business directly influences whether your content is eligible for citation in local AI answers.
Final Perspective
This is a beta preview with real limitations, no click data, no traffic attribution, sample-only grounding queries. But it represents a genuine structural shift: AI citation is now a measurable, trackable metric.
Once measurable, it becomes optimizable. Once optimizable, it becomes competitive.
Publishers who start tracking citation patterns now, and aligning content strategy with retrieval-layer signals, will have a meaningful advantage as GEO tooling matures across Bing, Google, and AI platforms throughout 2026.
FAQs On Bing AI Performance
What is the AI Performance dashboard in Bing Webmaster Tools?
It is a new public preview feature that shows publishers how often their content is cited as a source in AI-generated answers across Microsoft Copilot, Bing AI summaries, and select partner integrations. It tracks total citations, average cited pages, grounding queries, page-level citation activity, and visibility trends over time.
What are grounding queries in Bing Webmaster Tools?
Grounding queries are the internal retrieval phrases Bing’s AI system generates when searching for content to cite in an answer. They are not the exact user queries. They reveal how AI interprets topic intent and which phrases trigger content retrieval. Microsoft notes this data is a sample, not a complete log.
How does Bing AI Performance differ from Google Search Console AI reporting?
Bing offers a dedicated AI citation dashboard with page-level citation counts, grounding queries, and timeline trends. Google blends AI Overviews and AI Mode data into its standard Performance report without a separate dashboard, URL-level citation counts, or retrieval phrase visibility.
Does the Bing AI Performance report show click data?
No. The current preview only tracks citation frequency, how often your content is referenced as a source. It does not show clicks from AI answers, traffic impact, or conversion attribution. Microsoft has indicated more data will be added throughout 2026.
What is Generative Engine Optimization (GEO)?
GEO is the practice of optimizing content for citation and visibility within AI-generated answers, rather than traditional search engine rankings. Microsoft uses this term to describe the emerging discipline that the AI Performance dashboard is designed to support.
How does IndexNow help with AI citations?
IndexNow notifies participating search engines when content is added, updated, or removed. This enables faster discovery by AI retrieval systems, helping ensure that AI-generated answers reference the most current version of your content. IndexNow is supported by Bing, Yandex, Naver, Seznam, and Yep.