Businesses are under growing pressure to provide seamless, regional user experiences across borders as the internet continues to expand globally. Brands can now scale multilingual content at a never-before-seen speed thanks to the development of AI-powered content generation and translation tools. However, what role does AI play in how search engines like Google decide which version of your website to display to which user?
Welcome to the world of international SEO, AI translation, and the frequently misinterpreted but crucial hreflang tag. This blog examines how AI understands multilingual content, how hreflang helps to properly direct that content, and how companies can maximize their worldwide reach by utilizing AI-enhanced tactics.
Why International SEO Matters in 2025
Translating your content into several languages is only one aspect of international SEO. It involves optimizing your website so that search engines can determine which version of your page to display to a particular audience based on their location and language.
Even if they speak English as a second language, more than 75% of users worldwide prefer websites in their native tongue, according to Statista. There is a noticeable demand-supply gap because only 25% of the content on the internet is available in languages other than English.

Rise of AI Translation Tools
The quality of automatic translations has significantly increased thanks to AI tools like DeepL, Google Translate with Neural Machine Translation (NMT), and ChatGPT. Indeed, according to a 2023 study by CSA Research, AI-powered translations currently attain over 85% accuracy in vocabulary and sentence structure, particularly for pairs of European and Indo-European languages.
Because of this, AI is a desirable option for companies looking to expand internationally. However, there’s a catch: improper localization of AI-generated translations can negatively impact your SEO. Here’s where hreflang is useful.
What Is Hreflang, and Why Is It Crucial?
An HTML tag called the hreflang attribute is used to define a webpage’s language and geographic targeting. “This page is the French version for users in France,” or “This one is for Spanish speakers in Mexico,” are the messages it conveys to Google and other search engines.
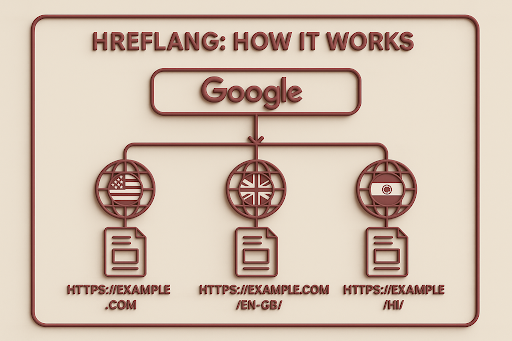
Why It Matters:
- Avoids problems with duplicate content on translated pages.
- Displays content in the user’s native tongue, improving the user experience.
- Increases international searcher engagement and CTR
- Aids in the correct indexation and delivery of relevant content by search engines.
When it comes to AI-powered content, hreflang makes sure that your multilingual AI-translated content reaches the correct audience and doesn’t compete with your original content.
How AI Handles Multilingual Content Interpretation
AI interprets, learns, and localizes in addition to translating. The most sophisticated AI models comprehend idioms, tone, cultural allusions, and regional subtleties through the use of Natural Language Processing (NLP) and machine learning.
However, there are restrictions:
- AI might overlook contextual tone or cultural sensitivities.
- Less widely spoken languages or dialects are difficult for it to understand.
- Unless directed by an SEO strategy, it does not automatically structure hreflang.
Content producers must combine human oversight, SEO accuracy, and AI efficiency to close this gap. This is particularly crucial when using AI to deploy multilingual pages, as hreflang tags still need to be manually added or configured using technical teams or plugins.
SEO Implications of AI Translation
AI translation is transforming cross-border brand communication, but it has complicated SEO ramifications as well. When used incorrectly, AI-driven translations can improve visibility or lower rankings based on factors like hreflang accuracy, keyword intent, and content consistency. Maintaining multilingual SEO integrity and guaranteeing discoverability in a variety of markets requires an understanding of how search engines process AI-translated content.
Risks:
- Duplicate content in the event that hreflang is not properly implemented.
- If translations are too literal or irrelevant, thin content penalties will be applied.
- Lack of keyword localization results in low rankings in local SERPs.
Rewards (if done right):
- Quick expansion of content into international markets.
- Increased organic traffic from users around the world.
- Increased domain authority through a variety of content.
Google’s own Search Central Blog states that if AI-generated content satisfies the requirements for useful, people-first content, it is not penalized. In actuality, Google’s algorithms are starting to prioritize value and intent over the author or source of the content.
But in order to be as visible as possible, you have to:
- Change titles, alt text, and meta tags according to the language.
- Make consistent use of hreflang tags throughout your multilingual structure.
- Steer clear of machine translation without post-editing.
Best Practices for International SEO in an AI-Driven Era
International SEO calls for more than just content translation in today’s AI-powered digital environment; it also calls for technical accuracy, intelligent automation, and strategic localization. Adopting best practices guarantees that your multilingual content ranks highly, resonates locally, and stays clear of common pitfalls as businesses use AI to scale globally. Here’s how to maximize international search engine optimization in an AI-shaped world.
Here is a brief guide to using SEO and AI to optimize global content:
- Draft with AI, then refine with local experts
The subtleties of local markets are beyond the comprehension of even the most advanced AI translation tools. When reviewing and modifying content, always use editors who speak the language.
- Properly Use Hreflang Tags
Make use of ISO codes (language-country formats such as en-us and fr-fr) and cross-reference each page’s alternate versions.
- Steer clear of auto-redirects Using IP Alone as the Basis
Geo-IP redirects are discouraged by Google. Allow users to select their preferred language using a selector, and use hreflang to direct search engines.
- Make Each Language’s URL Unique
To improve indexing, use subdirectories (e.g., /es/, /fr/) or subdomains (es.example.com) rather than query parameters (?lang=fr).
- Track Locale Performance
Track impressions, rankings, and click-throughs by region with Google Search Console’s international targeting and analytics.
Future of International SEO and AI
More tools that combine multilingual schema markup, AI-powered localization, and automatic hreflang tagging in a single workflow are anticipated in the future. Even if a user asks a question in one language and the best response is in another, Google’s Multitask Unified Model (MUM) already shows promise in translating and ranking content across languages.
Because of this, it is even more crucial that brands:
- Clearly organize their multilingual content.
- Consider the cultural context when localizing.
- Use hreflang and other precise SEO signals to direct Google.
Conclusion
The world is multilingual and AI-driven; it is no longer flat. The global content game will be won by brands that leverage the power of AI translation tools while firmly establishing their strategy around sound SEO principles like hreflang.
While AI lets you grow, hreflang makes sure the right people see your message.
The way forward is not AI or humans, as this international-seo-ai-translation-hreflang-guide has demonstrated. It is user-friendly, Google-structured, and combines AI and human insight.
Allow Oddtusk to assist you in scaling multilingual content without sacrificing rankings, reach, or meaning.





